Now Reading: How Do Tornadoes Form Step by Step?
-
01
How Do Tornadoes Form Step by Step?
How Do Tornadoes Form Step by Step?
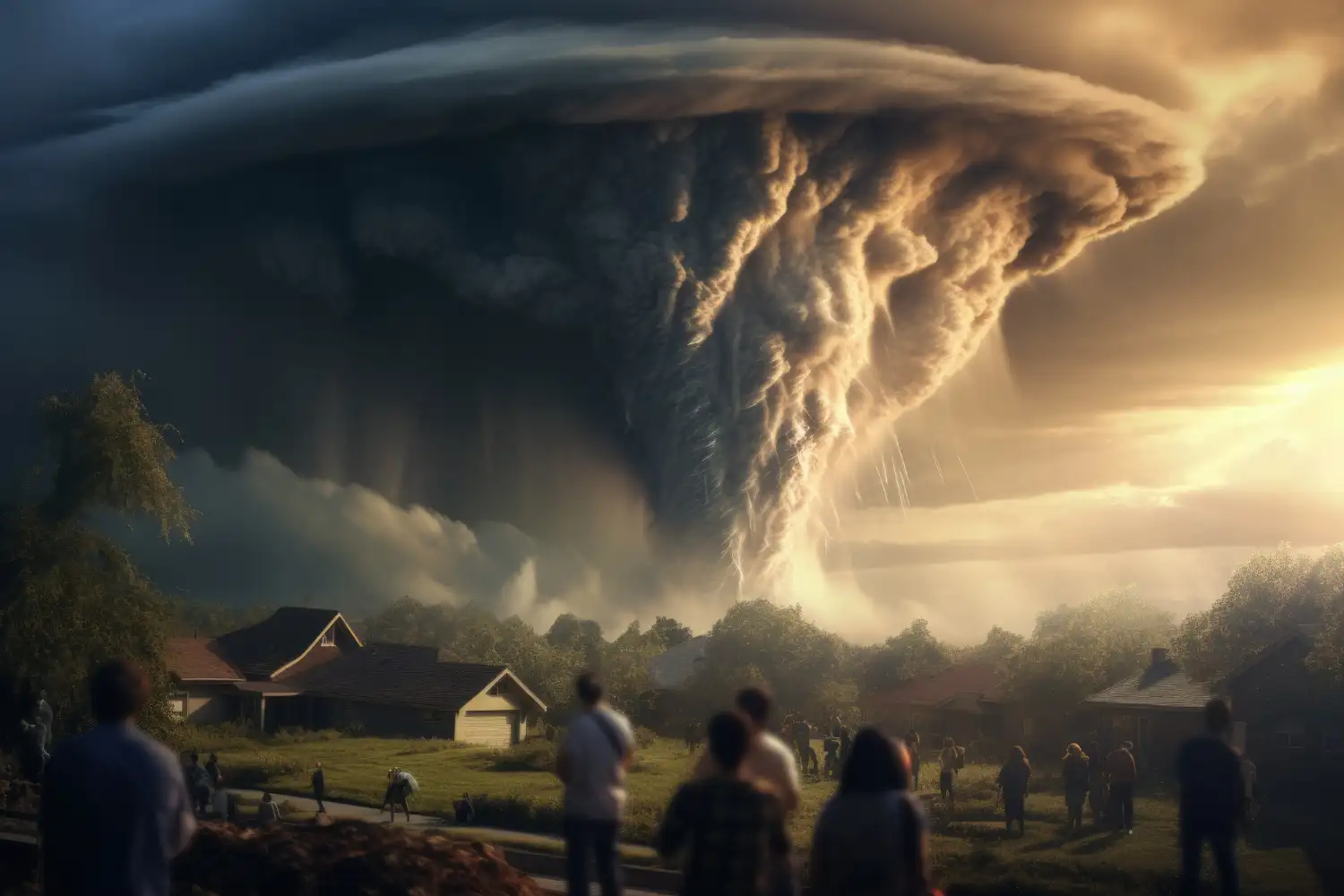

In 2025, 1,231 tornadoes hit the US, claiming 67 lives. Warm air rises, shear twists, downdrafts tighten the spin. This guide explains how do tornadoes form step by step with clear, fresh data. Scientists link warmer oceans to fiercer storms. New drones spot spins early for better warnings.
Tornadoes whirl like nature’s fierce dancers across the sky. In 2025, over 1,200 struck, taking 72 lives. So, how do tornadoes form step by step?
Warm, moist air pools low on steamy days. It pushes against cooler air above. As a result, tension brews for stormy clashes.
Moreover, wind shear adds the twist. Winds shift speed and direction upward. Consequently, air rolls like invisible tubes.
What Causes Tornadoes to Form
Heat and humidity start the storm’s engine. Warm air rises fast from hot ground. Meanwhile, cool air above holds it back.
But a front or heat breaks the cap. The warm air surges skyward. For instance, summer sun often triggers this lift.
In addition, shear spins the rising flow. It forms rolling tubes near the ground. Thus, what causes tornadoes to form blends these forces.
Supercell Thunderstorms and Tornadoes
Supercells stand as storm giants. They spin wide and last hours. Above all, most fierce tornadoes come from them.
Strong updrafts pull warm air high. Downdrafts push cold air beside. Therefore, rotation grows in a mesocyclone.
However, not all supercells spawn twisters. Dry air can kill the spin. In 2025, drones spot these failures early.

Formation of Tornadoes Explained
Air layers stack with contrast. Warm, wet bottoms face dry, cool tops. To clarify, this sets a stormy stage.
A push, like a front, sparks the rise. Updrafts soar, pulling air fast. Subsequently, clouds tower and darken.
Further, shear tilts horizontal rolls upright. The storm spins like a top. So, how do tornadoes form step by step? It’s a balanced dance.
How Tornadoes Develop in the Atmosphere
Skies hold the drama’s key. Jet streams whip cold air east. Meanwhile, slow surface winds drag south.
This gap shears air into rolls. Updrafts tip them vertical quick. As a result, spin surges in clouds.
In 2025, drones map these layers live. They show spins starting low. Thus, how tornadoes develop in the atmosphere relies on layered winds.
Tornado Diagram Explained
Diagrams clear up tornado chaos. A wide cloud base curves down. For example, warm arrows rise, cold ones sink.
Red swirls mark the mesocyclone’s turn. A thin funnel drops to dirt. To sum up, it shows the storm’s heart.
Moreover, 2025 apps animate these live. Satellites feed real-time sketches. Thus, tornado diagram explained makes the swirl simple.
Rotating Updraft and Downdraft
Updrafts twist when shear grabs hold. They spiral air inward fast. For instance, warm cores dodge rain longest.
Downdrafts flank with heavy, cool rain. They wrap the updraft tight. Consequently, rotation sharpens in the gap.
In addition, 2025 radars spot drop shapes. Hail signals stronger storms. So, rotating updraft and downdraft drive the twister.
Conservation of Angular Momentum in Tornadoes
Momentum stays fixed in air. Spinning parcels keep their share. Therefore, wide slow turns shrink to fast whirls.
Updrafts stretch the column thin. Speeds soar past 200 mph. In other words, it’s a skater tucking arms.
Likewise, 2025 sims model this well. Virtual spins match real storms. Conservation of angular momentum in tornadoes fuels the rage.
Spinning Air in Thunderstorms
Thunderstorms churn air like mixers. Clashing winds form low rolls. To illustrate, they align with ground gusts.
Updrafts lift rolls to vertical tubes. Heat pulses spin upward. Subsequently, the cloud turns whole.
Further, 2025’s wet spring boosted spins. La Niña fed extra moisture. Thus, spinning air in thunderstorms surged high.
Tornado Development Near the Ground
Spins spark low, near the dirt. Friction grinds air rough there. For instance, gusts collide to birth tiny whirls.
Warm inflows rush the storm’s base. Cool outflows shove from behind. As a result, a hook echo tightens.
In 2025, ground radars ping these early. They spot swirls yards above soil. So, tornado development near the ground warns fast.
Warm and Cool Air Gusts in Tornado
Gusts carry the storm’s clash forward. Warm southern flows haul moisture. On the other hand, cool northern blasts cut sharp.
They butt at the storm’s rim. Vorticity sparks like wheel friction. Therefore, the rear downdraft leads the chill.
Most importantly, balance keeps the spin alive. Warm must outpull the cool. Thus, warm and cool air gusts in tornado shape the whirl.
Figure Skater Effect in Tornado Rotation
Skaters show how spins speed up. Wide arms mean slow turns. But tuck tight, and whirls blur fast.
Tornado air mimics this tuck. Updrafts pinch the vortex slim. Consequently, momentum cranks winds to 250 mph.
In 2025, chasers filmed the squeeze. Clips prove the collapse. So, figure skater effect in tornado rotation drives the fury.
Why Some Supercells Don’t Produce Tornadoes
Supercells tease but often fail. Downdrafts flood the core too soon. For example, cold air smothers warm inflow.
Shear may weaken mid-storm. Rolls stay flat, no lift. In addition, dry wedges sap needed moisture.
In 2025, stats show 25% succeed. Climate shifts nudge more hits. Thus, why some supercells don’t produce tornadoes hinges on flaws.

Tornadoes and Wind Shear
Shear slices wind’s flow apart. Low breezes dawdle, highs race. As a result, rolls form in the gap.
Vertical shear tilts rolls to towers. Without it, storms stand stiff. To clarify, it’s the twist’s starter.
In 2025, March’s 299 twisters rode peak shear. Models map layers better. So, tornadoes and wind shear bond tight.
Strongest Type of Thunderstorm: Supercell
Supercells reign as storm lords. They knit tight, last hours. Above all, they birth the fiercest twisters.
Hail pelts like golf balls. Tornado tracks scar miles wide. For instance, winds hit 170 mph often.
In 2025, Missouri’s multi-vortex beasts wowed. Radars size hail exact now. Thus, strongest type of thunderstorm supercell rules severe.
| Stage | What Happens | Key Ingredients | 2025 Insights |
| 1. Instability Sets | Warm moist traps under cool lid. | Heat, humidity gap. | Warmer seas add steam. |
| 2. Trigger Lifts | Front or heat pops the cap. | Cold fronts, sun surge. | Early springs fire fast. |
| 3. Shear Rolls | Winds shift height, form tubes. | Vertical/horizontal shear. | La Niña boosts rolls. |
| 4. Updraft Tilts | Rise flips rolls to vertical. | Strong updraft pull. | Drones catch the flip. |
| 5. Downdraft Tightens | Rain chills, wraps spin tight. | Cool precip drop. | Radars spot surges quick. |
| 6. Funnel Drops | Funnel grips dirt with gusts. | Low drag whirls. | Ground radars warn early. |
In conclusion, this table maps the steps clear. Each phase builds on the last. Moreover, 2025 tech lights the path.
Tornadoes weave air’s wild tale. They form step by step from simple clashes. So, how do tornadoes form step by step? Warm rises, shear spins, balance bites.
Yet, 2025’s toll screams caution. Over 72 souls lost in the whirl. Therefore, heed warnings and duck fast.
To sum up, how do tornadoes form step by step? It’s a clash-to-twist saga. In short, science tames the fear.
Meanwhile, research races forward. New models predict the wild better. For example, 2025’s data sharpens the hunt.
FAQs
Tornadoes start with warm air rising under cool air, creating instability. Wind shear adds spin, tilting air into a rotating updraft. Downdrafts tighten the whirl near the ground, forming the funnel.
Wind shear creates horizontal rolling air. The updraft tilts it vertical, starting the spin. Without shear, storms lack the twist needed for tornadoes.
A supercell is a long-lasting storm with a rotating updraft. It often produces strong tornadoes. Shear keeps its parts separate for hours.
Many lack enough shear or moisture. Dry air can kill the spin early. Balance of ingredients decides if a twister forms.
Go to a basement or inner room fast. Cover with blankets or helmets. Avoid windows and cars if possible.

Ethan Cole is an American journalist with expertise across weather, tech, travel, and culture. With over 15 years of experience, he delivers sharp, reader-friendly stories that simplify complex topics and connect with audiences worldwide.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
-
 01Happy Gilmore 2: Your Complete Guide to the Golf Comedy Sequel
01Happy Gilmore 2: Your Complete Guide to the Golf Comedy Sequel -
 02Joe Root’s Test Runs: England’s Batting Genius in Focus
02Joe Root’s Test Runs: England’s Batting Genius in Focus -
 03The Bad Guys 2 (2025): Everything We Know So Far
03The Bad Guys 2 (2025): Everything We Know So Far -
 04Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba The Movie: Infinity Castle Tickets – Your Guide to the Epic Anime Event
04Demon Slayer: Kimetsu no Yaiba The Movie: Infinity Castle Tickets – Your Guide to the Epic Anime Event -
 05RTX 50 Series Unleashed: Next-Gen Gaming Power Awaits!
05RTX 50 Series Unleashed: Next-Gen Gaming Power Awaits! -
 06The Naked Gun 2025: What to Know About the Comeback Comedy Starring Liam Neeson
06The Naked Gun 2025: What to Know About the Comeback Comedy Starring Liam Neeson -
 07Freakier Friday 2025: Full Cast Breakdown, Plot Twists, Musical Throwbacks & Streaming Info
07Freakier Friday 2025: Full Cast Breakdown, Plot Twists, Musical Throwbacks & Streaming Info